- Homepage
- South America
- Amazon Rainforest
Facts About the Amazon Rainforest
Which Facts about the Amazon Rainforest are really important to know? Our Amazon Rainforest Facts were chosen and researched by kids especially for kids.

Facts about the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest is a unique ecosystem, that is often called the "lung of the earth".
The largest area of tropical forest on our planet, the Amazonas houses masses of trees and is rich with plants that provide oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide (CO2).
 Sunset over the Amazon rainforest
Sunset over the Amazon rainforestWhere is the Amazon Rainforest?
The Amazon Rainforest is located on the South American continent. About two thirds of the tropical rainforest is in Brazil, South America's largest country.
Moat of the Amazon rainforest is located in Brazil and eight neighbouring countries also share parts of the rainforest: Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, French Guiana and Suriname.
 The pristine Amazonas rainforest in Ecuador
The pristine Amazonas rainforest in EcuadorBrazil houses about 60% of the Amazon Rainforest, Peru about 13%, Colombia about 8% and Ecuador about 7%, the other countries share even smaller parts.
How big is the Amazon Rainforest?
The area of the Amazon rainforest is huge. About 5% of the land area of our planet are covered by the Amazon rainforest basin.
The area of the rainforest covers about 7 million square km/ 2.7 million square miles which is almost as large as the Oceanian country of Australia or twice as large as the land area of India on the Asian continent.
 Amazon rainforest seen from space
Amazon rainforest seen from spaceThe Amazon rainforest is almost as large (90%) as the contiguous US states, which means the USA without Alaska and Hawaii and the islands.
Compared to Europe and the UK, the Amazon rainforest is 75% of the EU land area but is about 28 times larger than the UK!
 Amazon river in Peru
Amazon river in PeruThe size of rainforest has a massive impact also on the earth's water cycle, as the many plant species of the Amazon region influence the amount of rain water and subsequently amount of water in the Amazon river as you will read below.
Amazon River Facts
The most important physical features of the Amazon rainforest is the Amazon River.
The Amazon is the largest river system in the world. Here are three basic facts about the Amazon:
- The Amazon river is the world's second longest river - after the Nile.
- The Amazon river is about 6,400 km/ 4,000 miles long.
- The Amazon river rises in Peru, flows through Colombia and Brazil and enters the Atlantic Ocean in Brazil.
Brazil Rainforest Biodiversity
Although the Amazon rainforest covers only about 5% of our planet's surface, more than 10% of all animals on our planet are home in the region.
 Amazon River
Amazon RiverThe Amazon region has an extremely high biodiversity and Brazil is the most megadiverse country in the world.
The Amazon rainforest contains about 30% of all animal and plant species on our planet. More primates live in this rainforest than anywhere else in the world.
 Megadiverse Brazil
Megadiverse BrazilThe Amazon region is home to about:
- 430 mammal species
- 420 amphibian species
- 380 reptile species
- 1,300 bird species
- 2,200 fish species and
- 2.5 million insect species.
About 40,000 plant species can be found here. And many more are still being discovered. On average one new species is discovered there every three days!
Amazon Rainforest - Climate
There is no distinct winter and summer season in the Amazonas.
The northern regions of the Amazon rainforest are hot and wet all year round. However, climate extremes are experienced in the Amazon region as well. Floods and droughts due to climate change are a dangerous challenge here.
The southern Amazon region where the deforestation rate is higher experiences longer dry seasons in recent years.
The climate in the largest city of the rainforest, Manaus, is tropical and the temperatures are high all year round. The annual monsoon between October and June brings strong rainfall.
Animals of the Amazon Rainforest
 Jaguar Jaguar |
The jaguar is Brazil's and Guyana's national animal. Most of these wild cats live in the Amazon basin. The night-active jaguars are the largest wild cats of the Americas. |
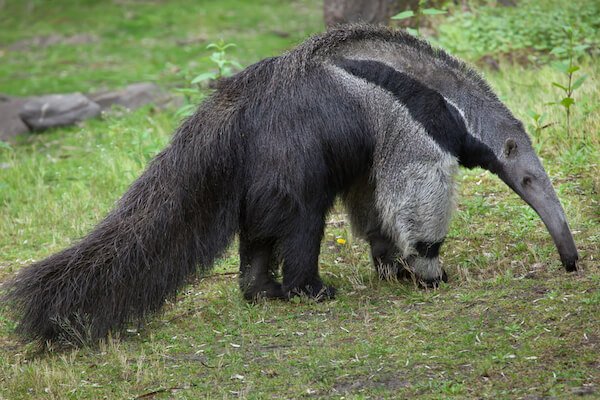 Giant anteater Giant anteater |
The giant anteater are almost blind but have a thick coat and claws to fight predators. They feed on insects and have no teeth. |
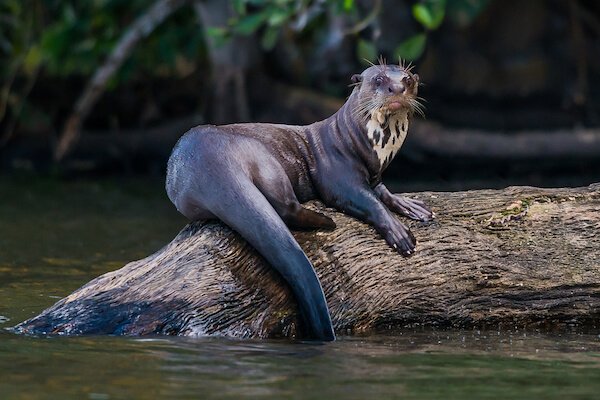 Giant river otter Giant river otter |
The giant river otter of South America is the largest otter species. The otter is referred to as 'water jaguar' in the local Tupi language. Their fur is very short and dense. |
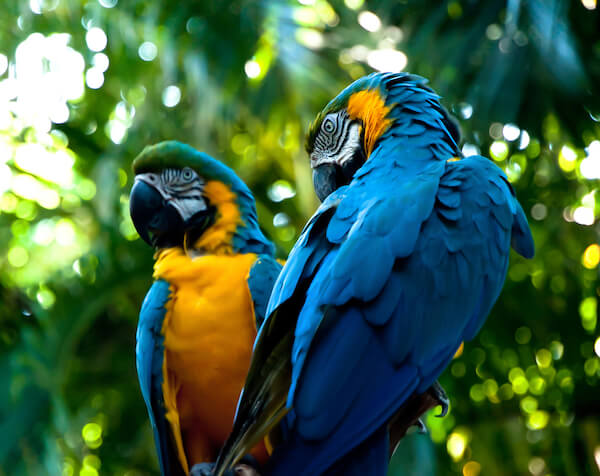 Macaws Macaws |
The macaw is the national bird of Brazil. The colourful parrots live in the rainforest and feed on seeds, fruits, vegetables and nuts. They were hunted for their feathers. |
 Arapaima Arapaima |
The Amazon river basin is home to over 2,000 fish species, among them the arapaima, which is air-breathing, and the famous piranha. |
Read more about animals in Brazil

People in the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest is home to about 47 million people.
Over 400 ethnic groups live in the Amazon rainforest region and more than 300 languages are spoken there.
The largest groups of indigenous people are the Tikuna and the Yanomami people in Brazil, the Waiwai or Warrao people of Guyana and the the Iquitos people in Peru.
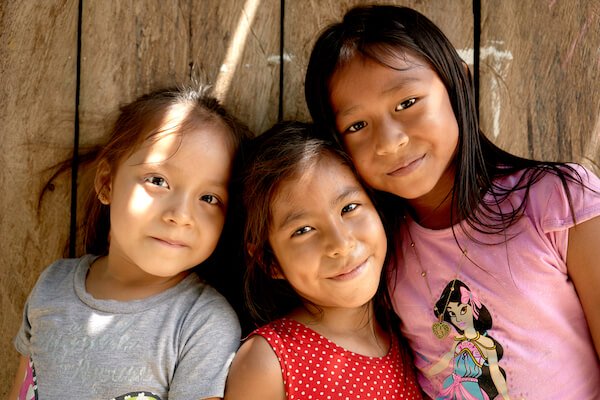 Children from the Iquitos ethnic group - image by Karol Moraes
Children from the Iquitos ethnic group - image by Karol MoraesSome of the most isolated tribes in the world can be found in the Amazonas region.
The Tagaeri and Taromenane in Yasuni National Park in Ecuador are among the last few indigenous people that live in complete isolation, but their livelihood is under threat due to exploration of the Amazonas resources.
The Amazon rainforest has only a few larger cities, most people live in rural villages and small communities.
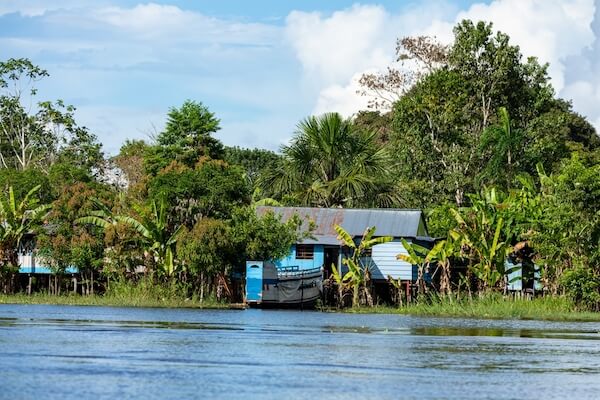 Amazon's iquitos houses
Amazon's iquitos housesThe largest city of the region is Manaus, which is home to about 2 million people. Manaus is also the capital city of Brazil's Amazonas state.
Manaus, Belem, Santarem and Iquitos are the largest and most populous cities in the Amazon rainforest.
The most important and largest city in the Amazon Rainforest is Manaus, a port city on the Amazon River.
 Manaus port - image by Gustavo Frazao
Manaus port - image by Gustavo FrazaoManaus is located centrally in the Amazon rainforest and about 1,450 km/ 900 miles from the Atlantic Ocean. However, the port city is the main transport link between the ocean and the western Amazon basin and used for hardwood timber exports.
Deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest
In the last 40 years, almost 20% of the Amazon rainforest has been lost! This is about the same size as the land area of France or the US state of Texas.
The land has been cleared for ranching of cattle, for plantations of palm trees or rubber trees or soy beans, logging and mining or is lost due to illegal logging or land grabs and speculation.
Every minute land area of the size of five football pitches are cleared!
 Soybean harvest in Mato Grosso/Brazil
Soybean harvest in Mato Grosso/BrazilThe deforestation from January to June 2022 was about three times higher than in the same 6-month period five years before.
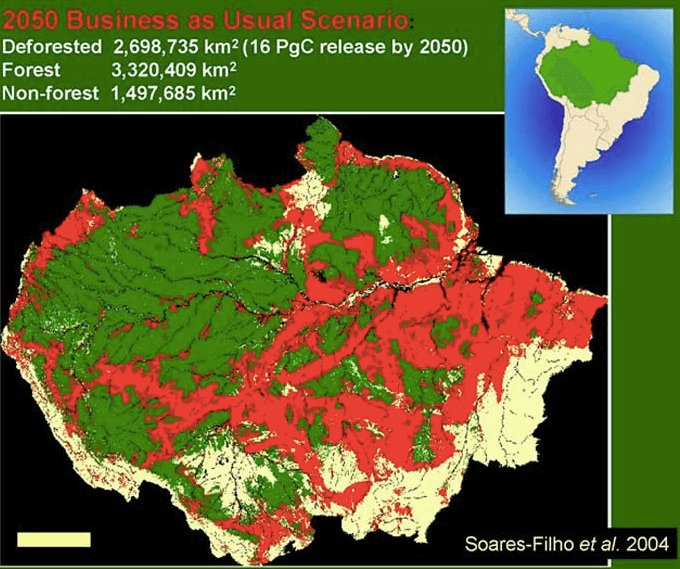
The ongoing deforestation threatens the biodiversity of the rainforest and sadly the rate of destruction is increasing. In the image below, you can see how much of the Amazon will be affected by deforestation and degradation by 2050.
Recent discovery of oil and gas under the Amazon will lead to further degradation of the region.
Facts about the Amazon Rainforest
Climate Change
The destruction of rainforest means that less carbon dioxide is cleared from the air and can be stored in the rainforest's fauna and less oxygen produced.
This means the rainfall cycle is impacted as less water is released by the trees which leads to a rise in temperature that then leads to dryer ares which are at higher risk of fire events and this will eventually lead to a dryer climate.
 Fire in the Amazonas region
Fire in the Amazonas regionThis shows that climate change is a vicious cycle and a sad reality.
Did you know that one single Amazon tree can release 1,000 litres of water into the air per day? The Amazon, however, is at threat due to increasing deforestation, exploitation and fires.
Facts about the Amazon Rainforest
Natural Resources
The main natural resources of the rainforest are timber, rubber, leather, beef and brazil nuts. Precious natural minerals are also found in the Amazonas region, among them iron ore, copper, tin, gold and kaolin.
Oil and gas is found in the eastern parts of the Amazon Rainforest. Oil and gas drilling is taking place in several parts of the region, such as in Ecuador, western Brazil and Guyana. About 93% of the oil imported to the USA from the Amazon region comes from Ecuador.
Mahogany and ipê are the most logged timber and used for decking, flooring and furniture. The foremost import country for Brazilian timber is the USA, followed by Mexico, China and the UK.
Facts about the Amazon Rainforest - Resources
- CSSP Brazil. "Investigating Future Rainfall Changes over Brazil." Metoffice.gov.uk. Last accessed 15 February 2023
- Greenpeace. "Brazil and the Amazon Rainforest". Greenpeace. Last accessed 15 February 2023.
- WWF. "Learn about the Amazon Rainforest." WWF. Last accessed 15 February 2023
- Jose A Marengo. "Drought, Floods, Climate Change, and Forest Loss in the Amazon Region: A Present and Future Danger?" Frontiers. 4 January 2020. Last accessed 15 February 2023
- Carlos Mazabanda. "Isolated Indigenous Peoples Under Threat of Oil Expansion". Amazon Watch. 2 November 2021. Last accessed 15 February 2023
- Philipp M. Fearnside. "Oil and gas project threatens Brazil's last great block of Amazon Rainforest." Mongabay. 9 March 2020. Last accessed 15 February 2023
Popular Pages
Competition Winners 2022
Images on Facts about the Amazon rainforest page: shutterstock.com and own images
Return from Facts about the Amazon Rainforest to Kids World Travel Guide Homepage
***