Animals in Brazil
There are many fascinating animals in Brazil. Let us tell you more about the fascinating fauna of this huge country in South America.
Brazil is known as the most megadiverse country in the world. This means Brazil houses the most animal species and the most plant species of any country in the world!
Which animals live in Brazil?
About one in five of all the plants and animals in this world are at home in Brazil.
Here we tell you about fifteen animals in Brazil you should have heard of.

Brazil is a huge country stretching over four time zones and several climatic regions with vastly different landscapes and habitats.
Brazil is the only country that has a reef environment in the South Atlantic. The Amazon river basin in Brazil is home to over 2,000 fish species, among them the arapaima, a fish that is air-breathing, and the famous piranha.
Here on Kids World Travel Guide we will tell you about these fifteen typical and unique animals in Brazil:
Rufous-Bellied Thrush
Let's start with a little animal from Brazil you should know, Brazil's national bird, the Rufous-bellied thrush. This thrush is a songbird native to the southeastern and eastern parts of Brazil.
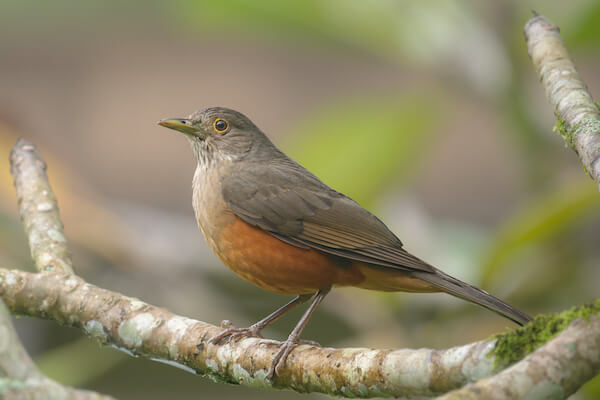 Rufous-bellied thrush
Rufous-bellied thrushThe Rufous-bellied thrush is a common bird in Brazil and feeds on tiny caterpillars, ants, seeds and fruits.
Their birdsong can be widely heard during the afternoons and during the night as the rufous-bellied thrush lives in the woodlands of urban areas.
Toucan
The toucan is a large bird with a broad colourful bill. Their name was given by the Tupi people of Brazil. The Tupí-Guarani word 'tuka' refers to the sounds or cry of the bird.
Brazil is home to about 15 of the world's 42 toucan species.
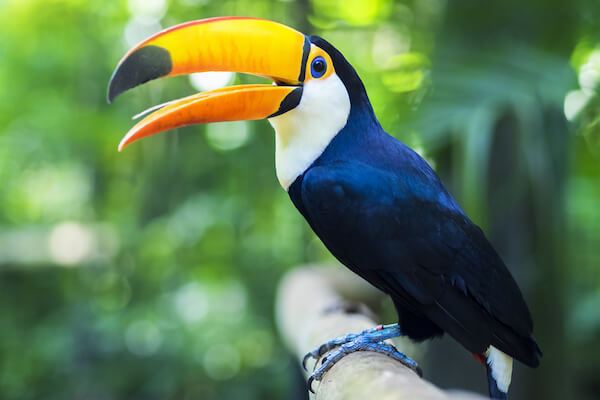 Toco toucan
Toco toucanThe toco toucan is the largest of the toucan species and grows up to 63 cm/ 25 inches in hight. It has an orange coloured beak that is 19 cm/ 7.4 inches long.
Toucans live in the rainforest and savanna (called Cerrado in Brazil) where they build nests in the hollows of trees. Their hatchlings are completely naked and do not have any feathers when they are born. The birds mainly live in pairs but can be seen in large flocks of up to 20 birds.
Piranha
The piranha is a freshwater fish that can be found in Brazil's rivers, mainly in the Amazon and the Orinoco river systems, floodplains and lakes.
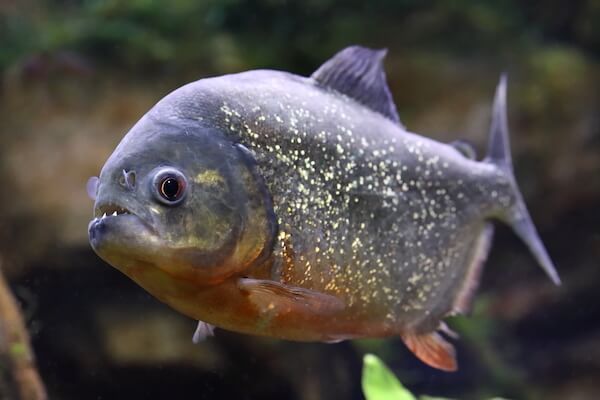 Piranha
PiranhaThe name piranha comes from the language of the Tupi people who named it "biting fish". The fish species is known for their strongest bite of all bony fish and they have large teeth and very strong jaw muscles.
Piranhas feed mainly on fish but also on plants, fruits and seeds. Although piranhas are described as aggressive fish, they are usually not dangerous to humans. Piranha attacks by large schools of fish are rare occasions.
In high-risk locations in Brazil, however, there are warning signs and sometimes nets have been installed for protecting beaches.
Rhea
The rhea is a large flightless bird or a South American ostrich. The rhea has grey brown feathers and long legs as well as a long neck. Rheas are smaller than emus and ostriches.
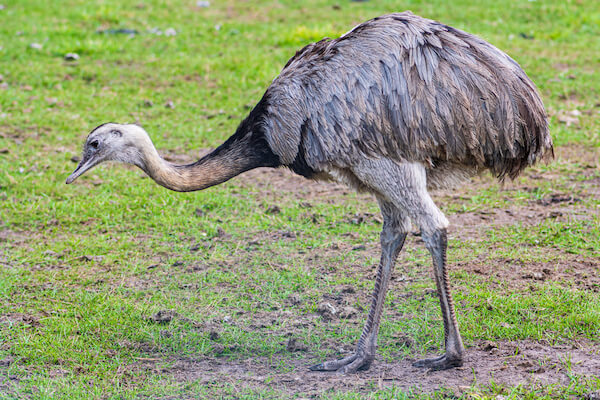

A rhea can weigh up to 40 kg/ 88 pounds. Rheas have three toes unlike other birds.
Rheas live in the grasslands of South America and can also be encountered in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay.
Rheas eat broad green leaves, seeds, fruit and berries as well as small insects.
Poison dart frog
There are over 170 species of poison dart frogs. These frogs live in humid tropical areas of the Brazil rainforest, in marshes, swamps, rivers or lakes.
Most poison dart frogs are small, some are as tiny as 1.5 cm/ 0.5 inch. Poison dart frogs are brightly coloured so they warn with their colour to ward off predators.
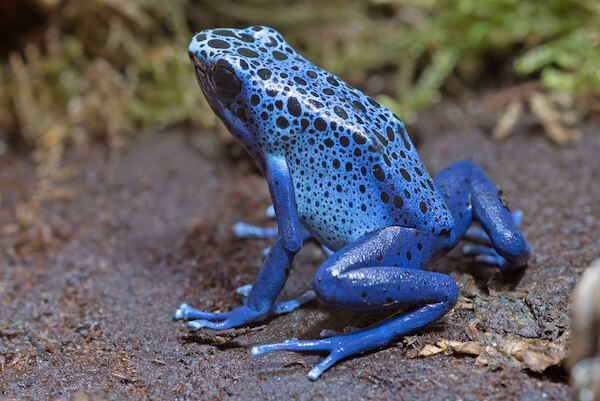 Blue poison dart frog
Blue poison dart frogThese colourful frogs get their name from the toxic substance they have in the glands of their skin that cover their whole body.
However, only very few species have a poison that can be dangerous to humans. When a predator tries to eat the frog, the toxin attacks the nerves of the predator and can cause death.
Some of the poison dart frogs are considered as threatened or endangered species.
These dart frogs received their name from the indigenous people who used the frog's venom as poison for the tips of their blow darts when using blow pipes for hunting.
Giant anteater - Animals in Brazil
The Brazilian anteater belongs to one of the largest anteater species. The mammals easily reach 2.2 m/ 7.2 ft in length and have a very long snout with a 60 cm/ 2 ft long tongue.
The sharp front claws are used to dig into anthills and termite nests. With its long tongue the anteater slurps up to 30,000 ants or termites each day.
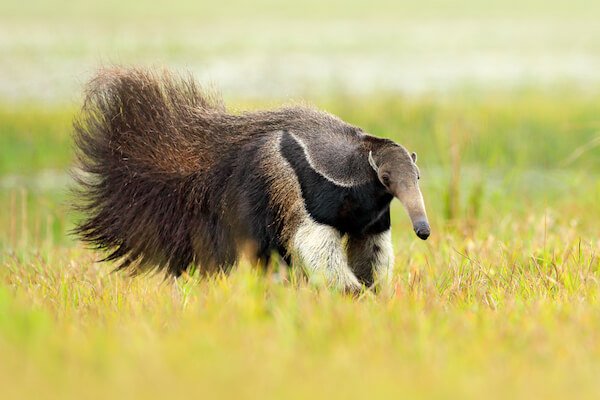 Giant anteater
Giant anteaterIn Brazil, the anteaters live in the Pantanal wetlands, open grasslands and the savannah (Cerrado). They live and hunt on the ground and they can climb trees.
Giant anteaters have a thick coat of fur and a very bushy tail. The mammal uses the tail at night to cover the body when it sleeps in a shallow hole in the ground, the tail serves as camouflage for the threatened species.
Jaguar
The largest cat species in the Americas is the jaguar.
The vulnerable species lives in the forests of Brazil, the Amazon rainforest as well as the Atlantic forests. Jaguars can also be found in open flood plains of the Pantanal and the savannah of the Cerrado.
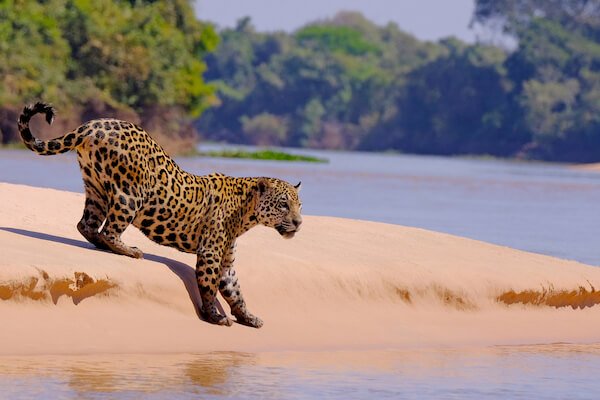 Jaguar in the Pantanal
Jaguar in the PantanalJaguars weigh up to 135 kg/ 298 pounds and have a yellow golden coat with black spots. Even black jaguars have these spots!
Each jaguar has its own variety of spots on the coat; these spots are unique just like human fingerprints.
Green anaconda
The green anaconda is one of the largest snake species and grows up to 9 m/ 30 ft long and can weigh up to 250 kg/ 550 lb.
 Anaconda snake
Anaconda snakeThis snake is green and has large dark spots. Anacondas live in Brazil mainly in the Amazon river basin and they can live also in water where they prefer slow moving shallow water such as in flooded grassland.
Adult anacondas can strike and devour large prey including capybaras and even jaguars.
Macaw - Animals in Brazil
Macaws are the world's largest flying parrots. These colourful birds live in the Amazon rainforest and tropical forested regions.
The largest species of macaws are the hyacinth macaws that can grow up to 102 cm/ 40 inches. All Macaws have long tail feathers. Here you see the colourful blue and yellow macaws that are common in Brazil, they grow up to 86 cm/ 34 inches tall.
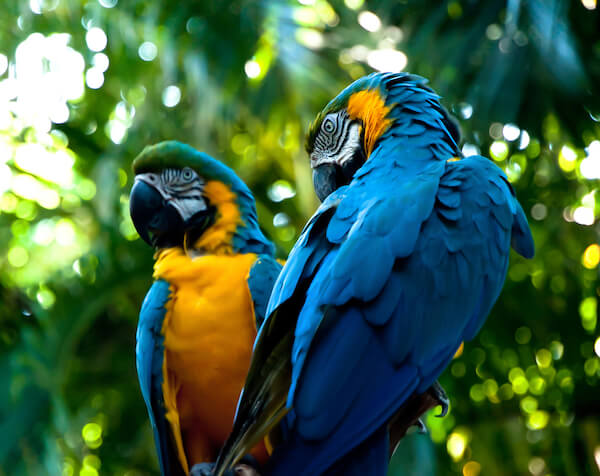 Macaw in Brazil
Macaw in BrazilMacaws feed on fruits, seeds and nuts. With their powerful beak muscles they can even crack open the hard shells of Brazil nuts. They can screech very loud when they feel threatened or disturbed.
Like most parrots, macaws can grow really old and some become 60 years or older.
Pink river dolphin
The pink river dolphin lives in the Amazonas. The animal is revered by the Brazilian people and is often called 'boto' which is their name in Portuguese.
The largest of the river dolphin species, the pink river dolphin can grow up to 2.7 m/ 9 ft. and weigh a massive 180 kg/ 400 lb.
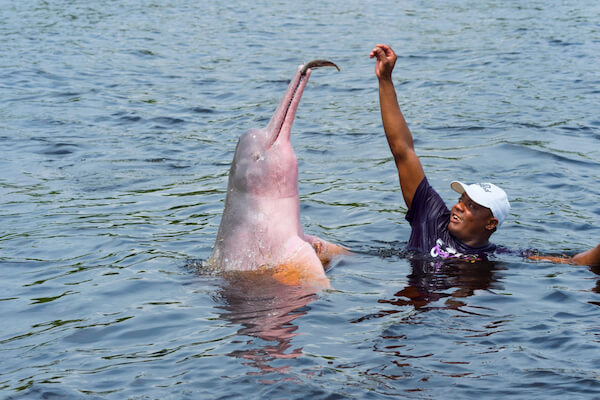 Brazil river dolphin in Manaus - image by GTW/ shutterstock.com
Brazil river dolphin in Manaus - image by GTW/ shutterstock.comThe endangered species is known for the unique pink colour, however baby dolphins are born grey and their skin colour only changes to pink when they become older. Pink river dolphin are known to get up to 30 years old.
Dolphins communicate via high frequency sonar sounds and clicks.
Golden Lion Tamarin Monkey
- Animals in Brazil
The Golden Lion Tamarin monkey is an endangered animal. The species lives in the rainforests along the Atlantic Coast of Brazil. There are only about 3,000 monkeys of this species left in the wild.
The Golden Lion Tamarin monkey has reddish orange hair with longer hair strands around the face. The species is quite small and grows only up to 26 cm/ 10 inches and weighs just over 500 g/ 1 lb.
 Golden Lion Tamarin Monkey with baby
Golden Lion Tamarin Monkey with babyThe monkeys are very aware of predators and change their nest every night. There they sleep up to 12 hours before they start roaming their surrounding area for fruits and insects and small vertebrates.
The Golden Tamarin monkeys tend to live in groups of two to eight family members. Tamarins usually give birth to twins and the babies are nursed and carried for four weeks.
Armadillo
The armadillo is native to Brazil and lives in the grasslands of the country's central state Mato Grasso.
The armadillo has a body that is covered in hard and bony keratin plates. Keratin is the material that is in our hair and nails. The three-banded armadillo has three strong back plates and can roll into a ball when it encounters predators.
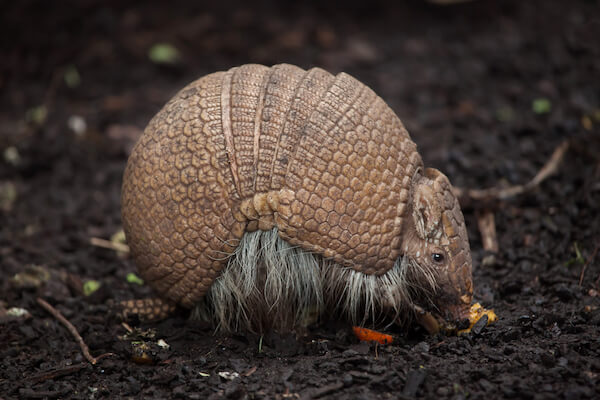 Three-banded armadillo
Three-banded armadilloThe Spanish colonialists gave the armadillo its name. They called it the "little armoured one".
The armadillo is a nocturnal animal with poor eyesight but with an excellent sense of smell. The mammal eats mainly ants, termites and larvae but enjoys sometimes ripe fruit.
Arapaima
The arapaima is the largest freshwater fish with scales in the world. Arapaimas grow up to 90 kg/ 200 lb and some species even reach 200 kg/ 400 lb. They can reach up to 4.6 m/ 15 ft in length.
In Brazil the fish is called pirarucu which refers to its colour as 'red fish' due to the red markings.
 Arapaima
ArapaimaThe sleek fish with a small head is unique as it can breathe air. Additional to the gills, the arapaima has a swim bladder with lung-like tissue. The fish therefore has to come to the surface to breathe air about every 10 minutes, which makes it vulnerable to predators or fishermen.
The massive fish is often called the 'dinosaur fish of the Amazon' as some 23-million-year-old fossils of the fish have been found, so it is one of the oldest known species of freshwater fish.
Sloth
The sloth is a nocturnal mammal, that sleeps about 15 hours each day. Sloths live high up in the trees of the Amazon rain forest and can sleep and eat upside down!
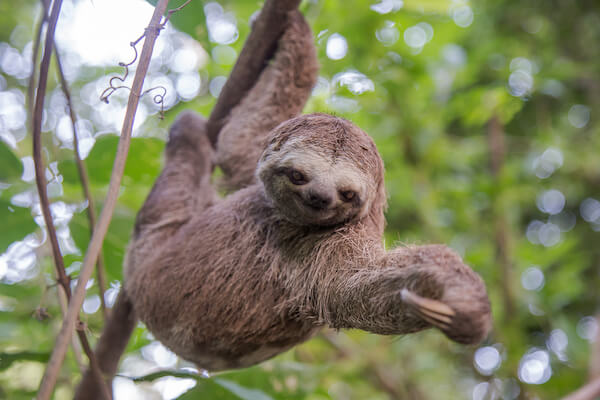 Sloth
SlothSloths mainly eat leaves, fruits and young green shots and have a slow metabolism, therefore they have little energy and move very slowly. These animals usually only move down from a tree about once a week - to poop!
These cute looking mammals are the size of a small dog and are common prey for jaguars and eagles.
Capybara
The capybara is the world's largest rodent. The mammal grows to about 1.2 m/ 4 ft in length and has long brown fur.
Capybaras are excellent swimmers and have been seen submerged under water for up to 5 minutes.
 Capybaras
CapybarasThe herbivore eats grasses, fruits and plants that grow in water. Capybaras live in densely forested areas near the water or in the Amazon rainforest in groups of 10 to 20 animals. Their average life span is seven years.
Capybaras are native to Brazil. They are found also in other South American countries, but not in Chile.
Caiman
The Yacare caiman lives in rivers, lakes or waters in the Pantanal and the Amazon rainforest.
About 10 million of these caimans live in the wetlands of the Pantanal!
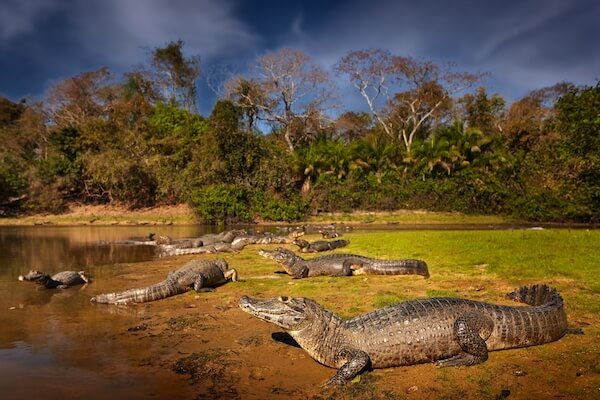 Yacare caiman
Yacare caimanThe Yacare caiman has brown coloured skin with dark brown spots or blotches.
The caiman species feeds on snails, fish and snakes but also eats smaller mammals such as capybaras. Caimans can get up to 40 years old!
Animals in Brazil
Resources for further reading
- An Qi. "How to differentiate the world's flightless birds." CGTN. 21 October 2019. Last accessed 23 August 2024
- Noah C. "The world of poison dart frog toxicity." ZooAtlanta. 18 February 2021. Last accessed 23 August 2024
- WWF. "The Giant Anteater." WWF. 11 June 2010. Last accessed 23 August 2024
- Smithsonian's National Zoo. "Giant Anteater." Smithsonian. Last accessed 23 August 2024
Popular Pages
Photo credits on Animals in Brazil page: Own images, wikicommons and Shutterstock images.
Return from Animals in Brazil to KidsWorldTravelGuide Homepage
More about Countries in
South America
KidsWorldTravels
Travel Guides
Spread the News